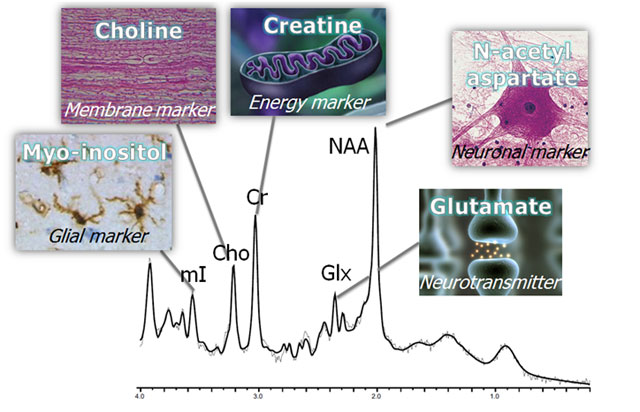
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is a powerful tool that examines brain metabolism using standard clinical MR scanners. A non-invasive and quantitative technique, MRS is ideally suited for repeated measurements and for measuring therapeutic outcomes. Often described as a “virtual biopsy”, MRS obtains chemical signals, or metabolites, from a region of interest (ROI or voxel). A spectrum of peaks is generated whereby each peak is reflective of a chemical that resonates at a specific frequency; the height of the peak reflects the concentration of that chemical in the brain (figure below).
Lactate is generally seen as a doublet (two peaks close together) at a frequency of 1.33 ppm. Again, healthy tissue does not have sufficient lactate to be detectable with MRS. However, CSF contains some lactate so that if the voxel is placed entirely in the ventricle, lactate may appear in the spectrum. Lactate, as a product of anaerobic glycolysis, is detected in diseased brain when oxygen starved. It is of great diagnostic value in cases of hypoxia, brain injury, and stroke. It is also elevated in some tumors where it is suggestive of aggressiveness as well as abscesses.
At 2.0 ppm, NAA is an amino-acid derivative synthesized in neurons and transported along axons. It is therefore a "marker" of viable neurons, axons, and dendrites27. The diagnostic value of NAA lies in the ability to quantify neuronal injury or loss on a regional basis and therefore, decreased NAA plays a diagnostic role in brain tumors, head injury, dementias, and many other neurological disorders in which neuronal loss is expected. Increased NAA is observed only in recovery and in Canavan disease that is due to a specific genetic disorder that reduces NAA-deacyclase activity resulting in net accumulation of NAA.
A mixture of closely related amino acids, amines and derivatives involved in excitatory neurotransmission lie between 2.1 and 2.4ppm. Glx is a vital marker(s) in MRS of stroke, lymphoma, hypoxia, and many metabolic brain disorders.
The primary resonance of creatine lies at 3.0ppm. It is the central energy marker of both neurons and astrocytes and remains relatively constant. For that reason, it is often used as an internal reference for comparison to other metabolites. While some studies have found Cr reduced, it is only in inborn errors of metabolism that significant reductions of Cr occur.
Choline includes several soluble components of brain myelin and fluid-cell membranes that resonate at 3.2ppm. Because by far the majority of choline-containing brain constituents are not normally soluble, pathological alterations in membrane turnover (tumor, leukodystrophy, multiple sclerosis) result in a massive increase in MRS-visible Cho.
A little known polyol (sugar-like molecules) that resonates at 3.6ppm, mI is mostly a diagnostic “modifier” in those diseases that affect Cho (tumor, MS, etc). As an astrocyte marker and osmolyte, mI contributes specificity in dementia diagnoses106, and an almost absolute specificity to hepatic encephalopathy and hyponatremic brain syndromes.
A number of additional brain metabolites can be measured with MRS, such as gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA), scyllo-inositol, glutathione, etc.; however, specialized editing sequences or additional software is required to detect and measure them and, therefore, they are beyond the scope of typical clinical practice. However, as MRS methods mature, they may soon be available to clinicians for assaying.
Please see the following reviews:
For over a century, a leader in patient care, medical education and research, with expertise in virtually every specialty of medicine and surgery.
About BWH